
To see the advantage, consider this example:Ī truck of mass m t is loaded with a heavy cargo of mass m c. For a multi-body system, however, there is a significant advantage in using momentum instead of velocity to describe the motion. Momentum is Additive in a Multi-Body Systemįor a single object, momentum and velocity are essentially equivalent since momentum is directly proportional to velocity. The units of momentum, as can be seen from its definition, are kg m/s. The direction of the momentum of an object is exactly the same as the direction of the object's velocity. It is important to note that momentum is a vector. Momentum (which is given the symbol p) is defined by:įor a single object of mass m traveling with velocity v. Properties of Momentum Definition in terms of Velocity Explain the advantage of momentum over velocity as the description of motion in a multi-body system.The law of conservation of momentum is applied to all the interactions including the separation and collisions that are caused by explosive forces.In this module, we define momentum and impulse.Īfter completing this module you should be able to:.

So, the change in momentum in one particle will be balanced by some other particle with an opposite and equal change in momentum.

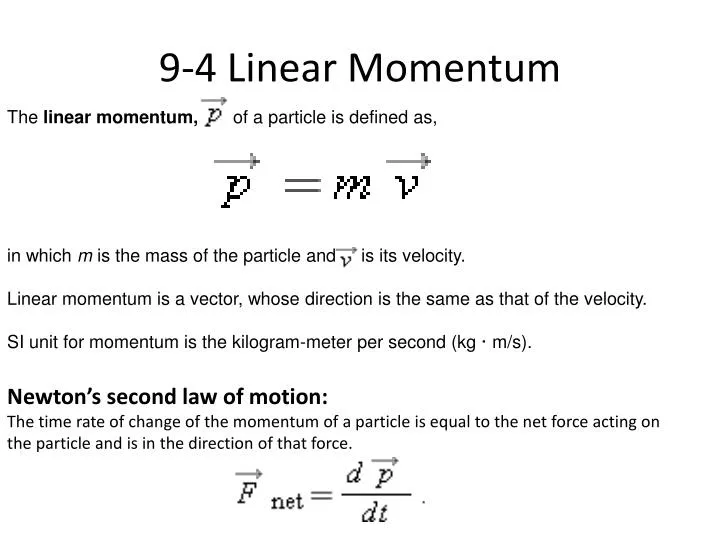
The dimensional formula of Linear Momentum can be denoted by.Linear Momentum units can be composed of the combination of mass(kg) and the velocity an object(ms -1) possesses.The Linear momentum SI units are apparently the same as the units of momentum.A vector quantity with only the measurement of the motion of objectects, Linear momentum can be expressed as the product of the mass of an object (m) and velocity (v).Linear momentum is also considered under the hierarchy of momentum. Assuming that either of the two values becomes zero, then the momentum also becomes zero. The momentum of a body generally depends upon both mass and velocity. What does the momentum of a body depend upon? In case of more than two particles, the momentum, will be added in following way: p = im i v i Hence the SI unit of momentum can be written as kg ms -1.įor two particles, the momenta can be added in the following manner: Hence, the SI unit that we get of the momentum of a body/ particle is the product of its mass (Kg) and its velocity (ms -1). The equation above describes the fact that the mass and velocity of the particle is directly proportional to the momentum of that particle. The mathematical equation of momentum of the object is, p = m \(\times\) v The momentum of a certain object is represented by the symbol ‘p’. So the derived SI Unit for momentum is kg ms -1. So, the mass is measured in kg and velocity is measured in ms -1. There is no particular name for the unit of Momentum as it is a product of velocity & mass whose units are expressed in quantities. Fundamental and Derived Units of Measurement


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
